Solar panels
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic systems (PV systems), use semiconductor technology to convert energy from sunlight into electricity that can power your household.

What kind of solar panels are used in a house?
Overall, monocrystalline panels are the best solar panel option for residential solar on the market today. However, you may want to consider polycrystalline or thin-film solar panels, depending on the size of your solar system and other needs.
How long do solar panels last?
25 years
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic or PV panels, are made to last more than 25 years. In fact, many solar panels installed as early as the 1980s are still working at expected capacity. Not only are solar panels remarkably reliable, solar panel longevity has increased dramatically over the last 20 years.
Solar panels typically don’t require much maintenance other than periodic cleaning and keeping them free from obstacles that can cast shadows over the panels. Solar panels need an unobstructed path to the sun to operate optimally.
Solar power is pollution-free and causes no greenhouse gases to be emitted after installation. Reduced dependence on foreign oil and fossil fuels. Renewable clean power that is available every day of the year, even cloudy days produce some power.


Why is solar important?
As a renewable source of power, solar energy has an important role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change, which is critical to protecting humans, wildlife, and ecosystems. Solar energy can also improve air quality and reduce water use from energy production.
Advantages of solar panel include
– Reduce electricity Bills
– Diverse applications
– Low maintenance cost
– Technology Development
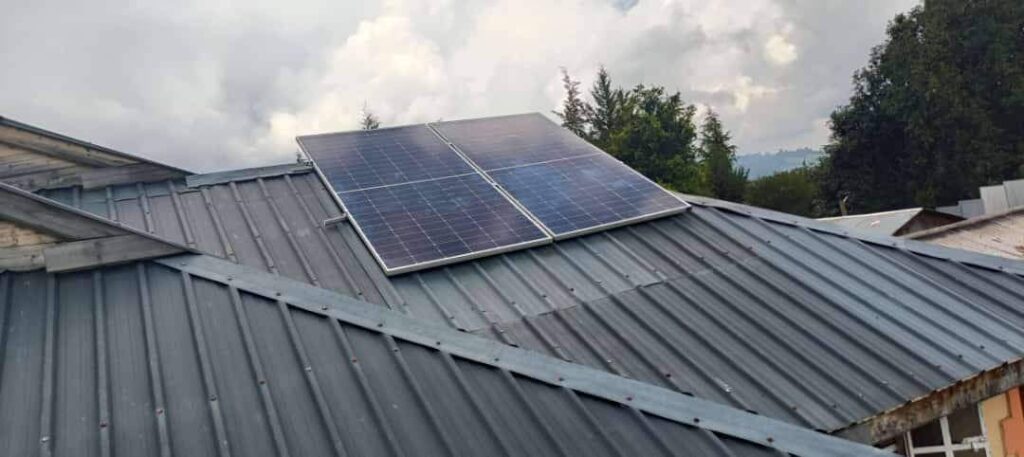
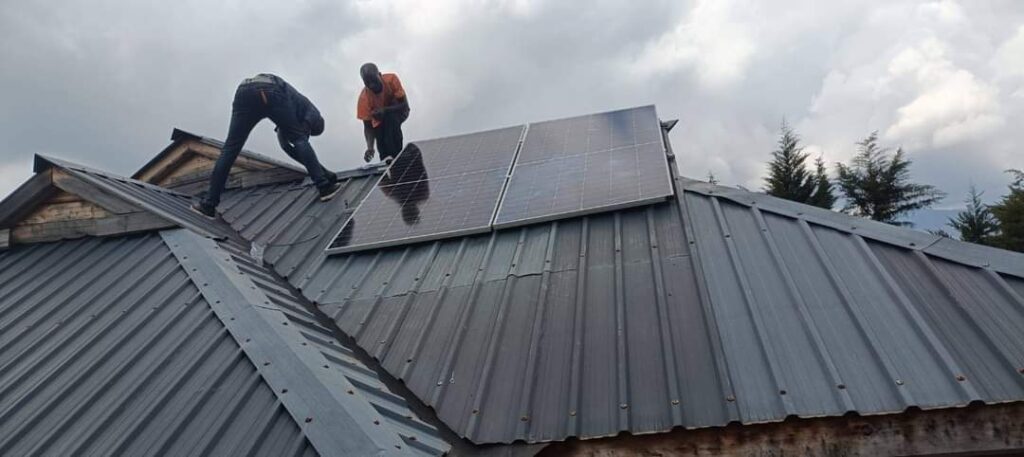


Solar panels provide numerous benefits, ranging from environmental advantages to cost savings and energy independence. Here’s a detailed look at the benefits of solar panels:
1. Cost Savings
- Reduced Energy Bills: Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, lowering your dependency on the grid and significantly reducing your energy costs.
- Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, or incentives to encourage solar adoption, further reducing installation costs.
- Long-Term Investment: Although the upfront cost can be high, solar panels provide long-term savings as they require minimal maintenance and can last 25–30 years.
2. Environmental Benefits
- Renewable Energy Source: Solar power is a clean and sustainable energy source that doesn’t deplete natural resources.
- Reduces Carbon Footprint: Solar panels produce no greenhouse gases or harmful emissions, helping combat climate change.
- Minimal Water Usage: Unlike traditional power plants, solar panels do not require water for operation, reducing strain on water resources.
3. Energy Independence
- Self-Sufficiency: Generating your own electricity reduces reliance on utility companies and protects against rising energy costs.
- Off-Grid Capability: Solar panels combined with battery storage allow homes and businesses to operate independently of the power grid, especially in remote areas.
4. Low Maintenance Costs
- Solar panels are durable and require minimal upkeep. Occasional cleaning and routine checks are usually sufficient to keep them running efficiently.
- Most manufacturers offer warranties of 20–25 years, ensuring reliable performance over time.
5. Increased Property Value
- Installing solar panels can increase the resale value of your home or property, as buyers are often willing to pay more for homes with reduced energy costs.
6. Job Creation and Economic Growth
- The solar energy sector contributes to local job creation, including manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of solar systems.
7. Scalability and Versatility
- Solar systems can be customized to meet your energy needs, whether for a small home or a large commercial building.
- Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, in open fields, or as part of solar farms.
8. Energy Reliability
- Solar panels can generate electricity even in cloudy or partial sunlight, depending on the system.
- With battery storage, you can store excess energy produced during the day and use it at night or during outages.
9. Reduces Grid Strain
- By generating electricity locally, solar panels reduce the demand on power grids, especially during peak usage times, leading to fewer outages and better energy efficiency.
10. Supports Clean Technology Innovation
- Investing in solar energy encourages the development of advanced, efficient technologies and promotes a transition to sustainable energy systems.
11. Noise-Free Operation
- Unlike generators or wind turbines, solar panels operate silently, making them ideal for residential and urban environments.
12. Tax Benefits and Incentives
- Many regions offer tax credits, deductions, or grants to offset the installation costs of solar systems.
- Net metering programs allow homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid, generating additional savings.
Conclusion
Solar panels offer significant environmental, financial, and energy benefits. They are a smart, sustainable choice for individuals and businesses looking to reduce energy costs, minimize their environmental impact, and achieve energy independence.
Would you like assistance in choosing a solar panel system or exploring specific brands or types?
Types of solar batteries you might need to consider when installing Solar Panels
1. Lithium Ion
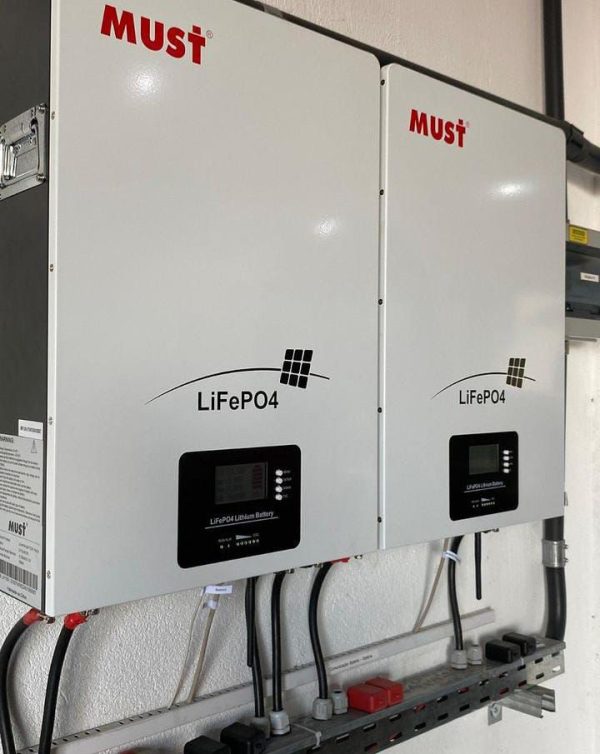
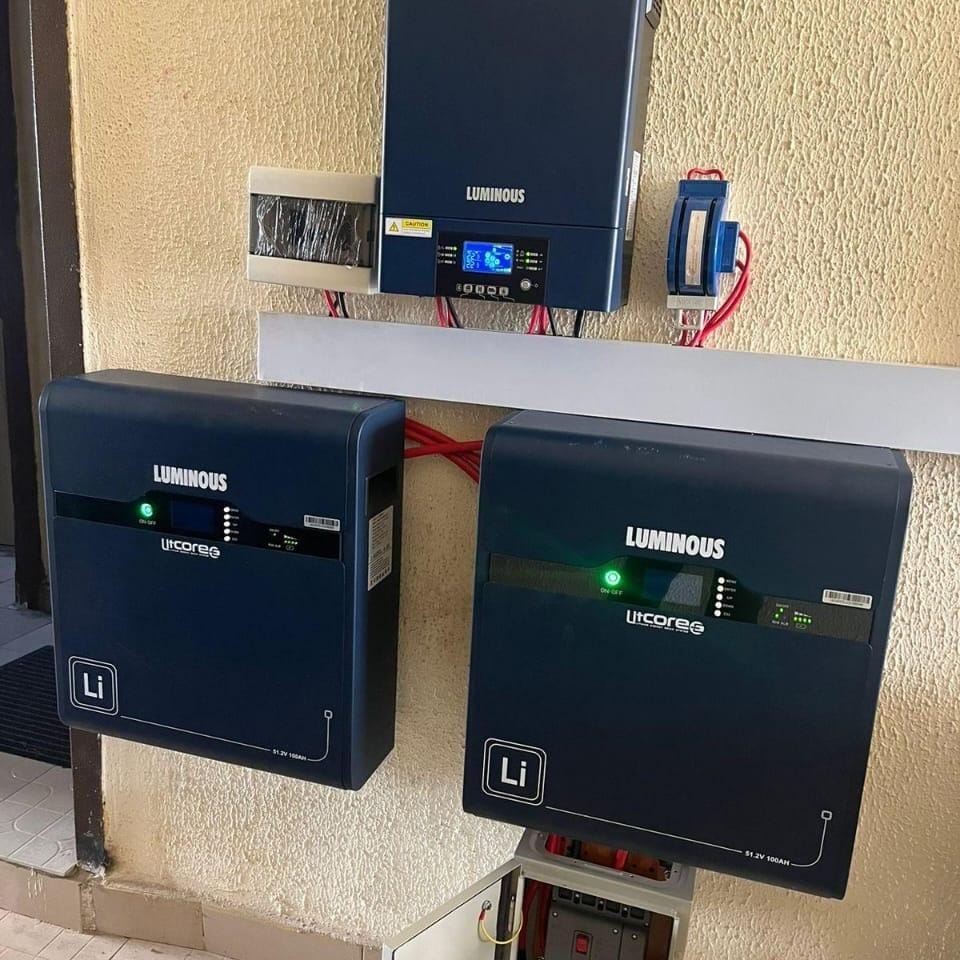




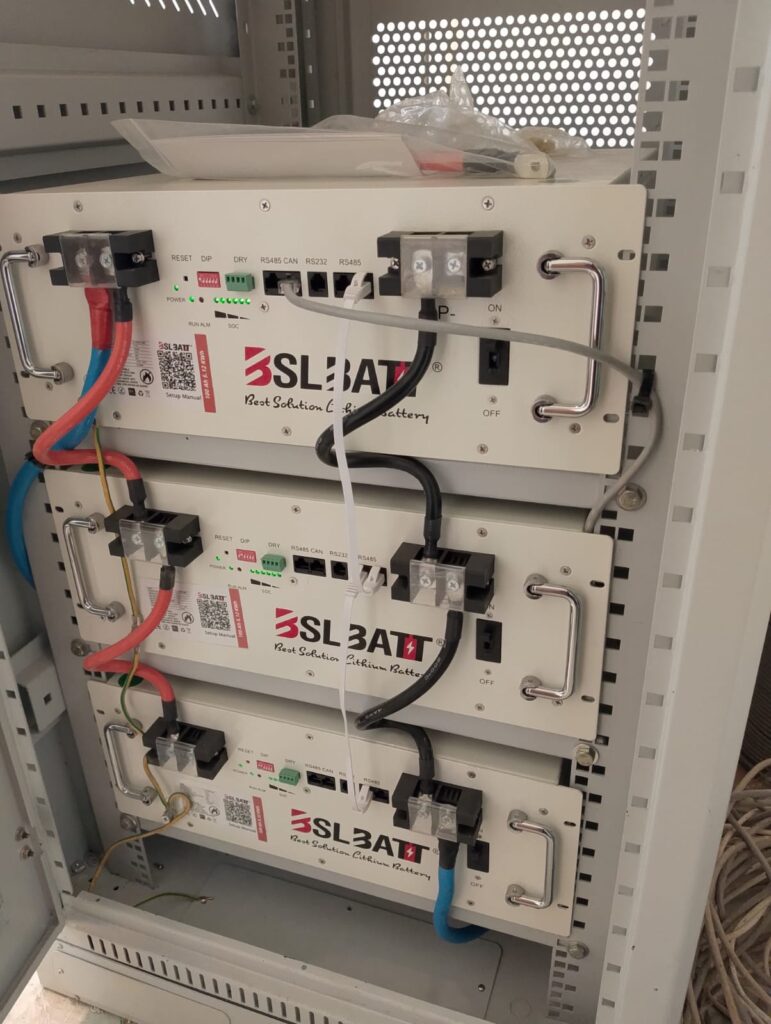



Lithium-ion solar batteries are one of the most efficient and reliable energy storage solutions for solar power systems. They store the energy generated by solar panels for use when the panels aren’t producing electricity, such as during the night or cloudy days. Here’s a detailed overview of lithium-ion solar batteries, their features, and benefits:
Key Features of Lithium-Ion Solar Batteries
High Energy Density
- Lithium-ion batteries can store more energy in a compact space compared to other types like lead-acid batteries.
Long Lifespan
- They typically have a lifespan of 10–15 years or more, depending on usage and maintenance.
- Cycle life is higher (up to 5,000–10,000 cycles), meaning they can be charged and discharged many times without significant capacity loss.
Efficient Charging and Discharging
- Lithium-ion batteries have higher round-trip efficiency (90–95%), meaning less energy is lost during the charge/discharge process.
- They support fast charging, which is useful when solar production is high.
Lightweight and Compact
- Lithium-ion batteries are lighter and smaller than alternatives like lead-acid, making them easier to install and handle.
Low Maintenance
- Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries do not require regular maintenance, such as adding water or checking acid levels.
Benefits of Lithium-Ion Solar Batteries
Energy Independence
- Allows for reliable energy storage, making you less dependent on the grid, especially during blackouts or peak hours.
Higher Usable Capacity
- Lithium-ion batteries can discharge up to 80–100% of their capacity without affecting performance, unlike lead-acid batteries that are limited to 50%.
Environmental Benefits
- Lithium-ion batteries are more environmentally friendly as they last longer and reduce the need for frequent replacements, minimizing waste.
Scalability
- These batteries are modular, meaning you can add more batteries to increase storage capacity as your energy needs grow.
Durability and Resilience
- Can operate efficiently in a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for different climates.
Supports Modern Technology
- Lithium-ion batteries integrate easily with smart solar systems, allowing for remote monitoring, optimization, and better energy management.
Types of Lithium-Ion Batteries for Solar
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4)
- High safety, thermal stability, and longer lifespan compared to other lithium-ion chemistries.
- Widely used in solar applications due to its reliability.
Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
- Offers a balance of energy density and safety, commonly used in residential and commercial setups.
Applications of Lithium-Ion Solar Batteries
Residential Solar Systems
- Store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during outages.
Off-Grid Systems
- Essential for homes or businesses in remote areas without grid access.
Commercial and Industrial Use
- Store energy during off-peak hours and reduce reliance on costly grid electricity during peak times.
Backup Power
- Serve as a reliable backup during blackouts or emergencies.
Advantages Over Lead-Acid Batteries
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Lead-Acid Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Low |
| Lifespan | 10–15 years | 3–5 years |
| Maintenance | Low | High (regular maintenance) |
| Depth of Discharge | 80–100% | ~50% |
| Efficiency | 90–95% | 70–80% |
| Weight | Light | Heavy |
Popular Lithium-Ion Solar Battery Brands
Tesla Powerwall
- Sleek design, scalable capacity, and advanced energy management features.
LG Chem RESU
- Compact and reliable, ideal for residential use.
BYD Battery-Box
- Modular design, high performance, and excellent scalability.
Pylontech
- Affordable and widely used in off-grid solar setups.
Simpliphi Power
- Focus on safety, reliability, and environmentally friendly materials.
Sonnen Battery
- High-end smart batteries with excellent energy management systems.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion solar batteries are a game-changer for energy storage, offering high efficiency, durability, and flexibility. They are ideal for residential, commercial, and off-grid solar systems, enabling users to maximize solar energy usage and achieve greater energy independence.
Would you like guidance on selecting the best lithium-ion battery for your solar system?
2. Lead Acid Battery















Lead-acid batteries have been a traditional choice for solar energy storage systems for decades due to their affordability and reliability. However, they have some limitations compared to newer technologies like lithium-ion batteries. Here’s a detailed review of lead-acid batteries for solar applications:
Types of Lead-Acid Batteries
Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA) Batteries
- Require regular maintenance, such as adding distilled water and cleaning terminals.
- Affordable and durable but need proper ventilation and cannot be tilted or placed indoors.
Sealed Lead-Acid (SLA) Batteries
- Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM): Maintenance-free and spill-proof, offering better performance than flooded types.
- Gel Batteries: Also maintenance-free and spill-proof, with better performance at deep discharges.
Advantages of Lead-Acid Batteries for Solar
Affordability
- Lead-acid batteries are significantly cheaper upfront than lithium-ion batteries, making them accessible for budget-conscious users.
Proven Technology
- Well-established and reliable, with decades of use in solar and other energy storage applications.
High Surge Current
- Capable of handling high surge currents, which can be beneficial for applications requiring sudden bursts of power.
Recyclability
- Lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable, with well-established recycling programs in place globally.
Limitations of Lead-Acid Batteries
Short Lifespan
- Typically last 3–5 years, much shorter than lithium-ion batteries, especially with frequent deep discharges.
Low Depth of Discharge (DoD)
- Can only be discharged to about 50% of their capacity to prevent damage, reducing the usable energy.
Efficiency
- Lower round-trip efficiency (70–80%) compared to lithium-ion batteries (90–95%).
Maintenance Requirements
- Flooded lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, including water refills and cleaning, adding to operational effort.
Weight and Size
- Heavier and bulkier than lithium-ion batteries, requiring more space and making installation more challenging.
Sensitivity to Temperature
- Performance decreases in extreme temperatures, and they require proper ventilation to avoid overheating.
Applications Where Lead-Acid Batteries Are Suitable
Off-Grid Solar Systems on a Budget
- Ideal for users who prioritize affordability over lifespan or energy efficiency.
Backup Power
- Effective for occasional use in backup systems where deep cycling isn’t frequent.
Remote Locations with Minimal Energy Needs
- Suitable for applications with low energy requirements and where regular maintenance is manageable.
Comparison with Lithium-Ion Batteries
| Feature | Lead-Acid Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Upfront Cost | Low | High |
| Lifespan | 3–5 years | 10–15 years |
| Depth of Discharge | ~50% | 80–100% |
| Efficiency | 70–80% | 90–95% |
| Maintenance | High (Flooded type) | Low |
| Weight and Size | Heavy and bulky | Lightweight and compact |
| Temperature Tolerance | Moderate, requires ventilation | Better tolerance and adaptability |
Advantages of Flooded vs. Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries
| Feature | Flooded Lead-Acid | Sealed Lead-Acid (AGM/Gel) |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance | Maintenance-free |
| Cost | More affordable | Slightly higher upfront cost |
| Lifespan | Shorter due to high maintenance | Longer due to sealed design |
| Installation | Requires ventilation and upright position | Flexible installation options |
Key Brands for Lead-Acid Solar Batteries
Trojan
- Known for high-quality deep-cycle flooded and AGM batteries.
Renogy
- Offers cost-effective AGM batteries for solar systems.
Deka
- Produces reliable AGM and gel batteries with good performance.
Exide
- Well-established brand offering both flooded and sealed lead-acid batteries.
Varta
- Focuses on sealed AGM batteries for clean and maintenance-free operation.
When to Choose Lead-Acid Batteries
- If you are on a tight budget and can handle regular maintenance.
- For systems with low daily energy requirements and minimal deep cycling.
- In areas where battery recycling programs are easily accessible.
Conclusion
Lead-acid batteries remain a viable choice for solar energy storage, particularly for those prioritizing affordability over performance. However, their lower lifespan, lower efficiency, and higher maintenance requirements make them less ideal for modern, high-demand applications compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Would you like recommendations for a specific type of lead-acid battery for your solar system?

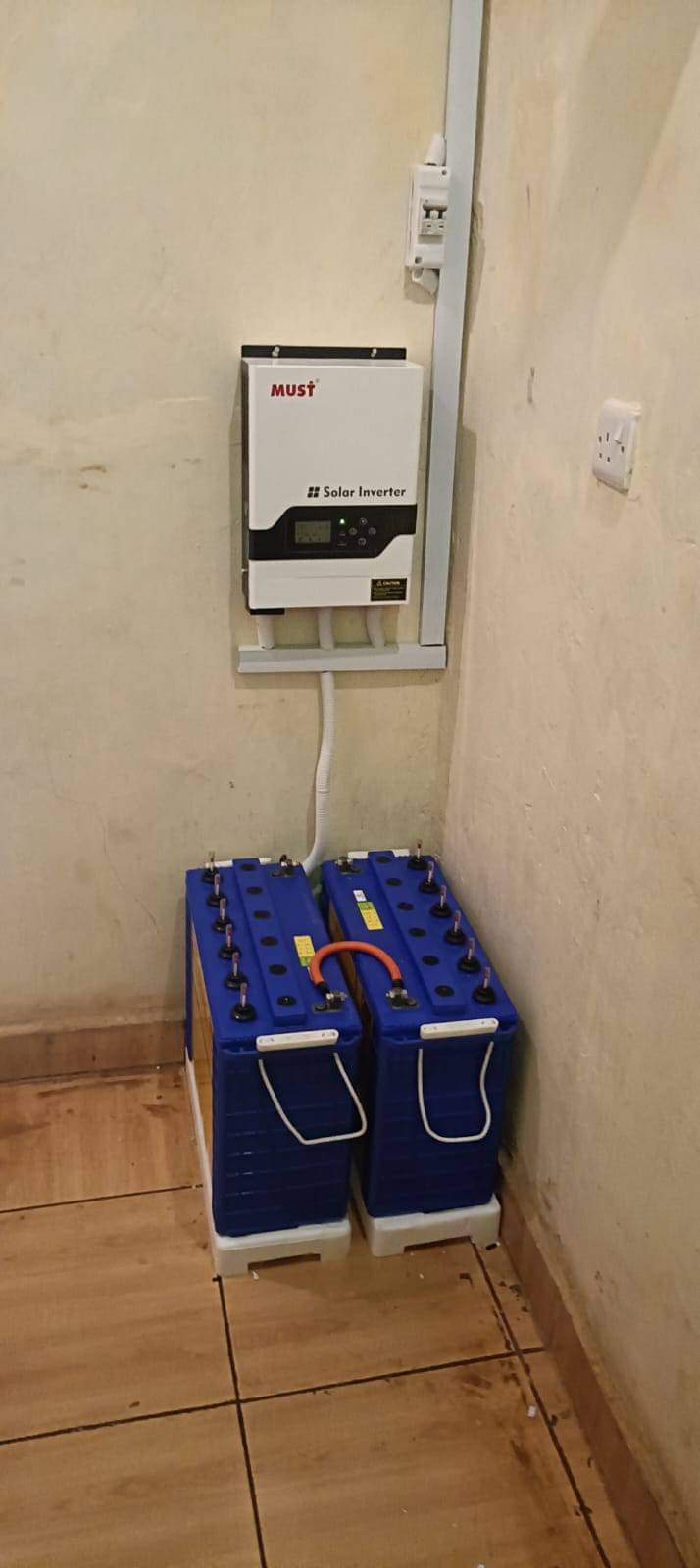
Hybrid Inverters















A solar hybrid inverter is a key component in modern solar power systems, combining the functions of a solar inverter and a battery inverter. It enables solar power to be used efficiently while also allowing energy storage in batteries for later use. This technology provides several advantages, especially in off-grid or grid-tied systems with energy storage.
Here’s a breakdown of how a solar hybrid inverter works and its main functions:
1. Energy Conversion (Solar Inverter Function)
- Solar Panel DC to AC Conversion: Solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity. The hybrid inverter first converts this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which can be used to power home appliances and other electrical devices.
- Maximizing Solar Energy Use: The inverter ensures that the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is employed to optimize the conversion of solar energy, adjusting for changes in sunlight conditions.
2. Battery Charging and Discharging
- Battery Charging: The hybrid inverter is equipped with an integrated battery charger. When the solar panels generate more power than is needed for immediate use, the excess energy is directed to the batteries for storage. The inverter controls the flow of energy to the batteries, ensuring they are charged efficiently and safely.
- Battery Discharging: When solar power is not available (e.g., during the night or on cloudy days), the inverter pulls energy from the batteries. It then converts this stored DC energy into AC power for use by the home or business.
3. Grid Interaction
- Grid-Tied Systems: In a grid-connected hybrid solar system, excess solar power can be fed back into the grid. The hybrid inverter manages this by converting the DC power generated by the solar panels into AC power and synchronizing it with the grid’s voltage and frequency. The inverter ensures that power flows in the correct direction and that the system operates in compliance with grid regulations.
- Energy Export: If your hybrid inverter is connected to a grid, you can sell excess power back to the grid or receive credit for the energy you export (through net metering programs).
4. Smart Energy Management
- Energy Prioritization: The hybrid inverter can intelligently manage the flow of energy, ensuring that your home or business always has power when needed. It prioritizes the use of solar energy first, followed by battery storage, and finally, grid power if necessary.
- Self-Consumption Optimization: In hybrid systems, the inverter allows you to maximize self-consumption of solar energy by minimizing grid reliance. This reduces your electricity bill by using your own solar power as much as possible.
5. Backup Power Functionality
- Power Outage Protection: One of the key features of a hybrid inverter is the ability to provide backup power during a grid failure. When the grid goes down, the inverter can automatically switch to off-grid mode using the energy stored in the batteries. This is essential for systems in regions with unreliable electricity supply or where grid failures are frequent.
- Seamless Transition: In the event of a blackout, the hybrid inverter ensures a seamless transition to battery power, so you don’t lose electricity for critical appliances.
6. Communication and Monitoring
- Remote Monitoring: Hybrid inverters typically come with monitoring systems that allow users to track energy generation, consumption, battery levels, and more. Some systems enable remote monitoring via smartphone apps, making it easy to adjust settings, check system performance, or troubleshoot issues.
- Integration with Smart Grids: In some advanced systems, hybrid inverters can communicate with the grid or smart devices to optimize energy use dynamically based on demand, pricing, and availability.
Key Components of a Hybrid Solar Inverter
- DC-AC Conversion Unit: Converts the DC power from the solar panels and/or batteries into usable AC power.
- Battery Charge Controller: Regulates the flow of energy to and from the battery bank, ensuring safe and efficient charging and discharging.
- Energy Management System (EMS): Controls the distribution of energy between the solar panels, batteries, and grid, optimizing self-consumption and battery use.
- Grid Interface: Synchronizes the system with the grid to manage exports and imports of electricity when the system is grid-tied.
Benefits of Hybrid Solar Inverters
- Flexibility and Energy Independence: You can use solar power day and night, store energy for later use, and minimize reliance on the grid.
- Reduced Energy Costs: By storing excess solar energy in batteries, you can use it during high-cost periods (such as at night or during peak hours), cutting your energy bills.
- Environmental Impact: Hybrid inverters allow you to maximize the use of renewable solar energy, reducing your reliance on fossil fuels.
- Scalability: Many hybrid inverters are modular, meaning you can expand the system by adding more batteries or solar panels over time.
- Backup Power: In areas with frequent power outages, hybrid inverters provide a reliable backup solution, ensuring your home or business has power even during grid failures.
- Energy Monitoring and Smart Management: Advanced hybrid inverters come with energy management software that allows you to monitor your system’s performance and optimize energy consumption in real-time.
Conclusion
A solar hybrid inverter is a highly efficient solution for managing solar power generation, battery storage, and grid interaction. It allows you to optimize energy use, reduce reliance on the grid, and maintain backup power during outages. By combining solar and battery management into one unit, hybrid inverters provide a more seamless, reliable, and cost-effective solution for solar energy storage and consumption.
